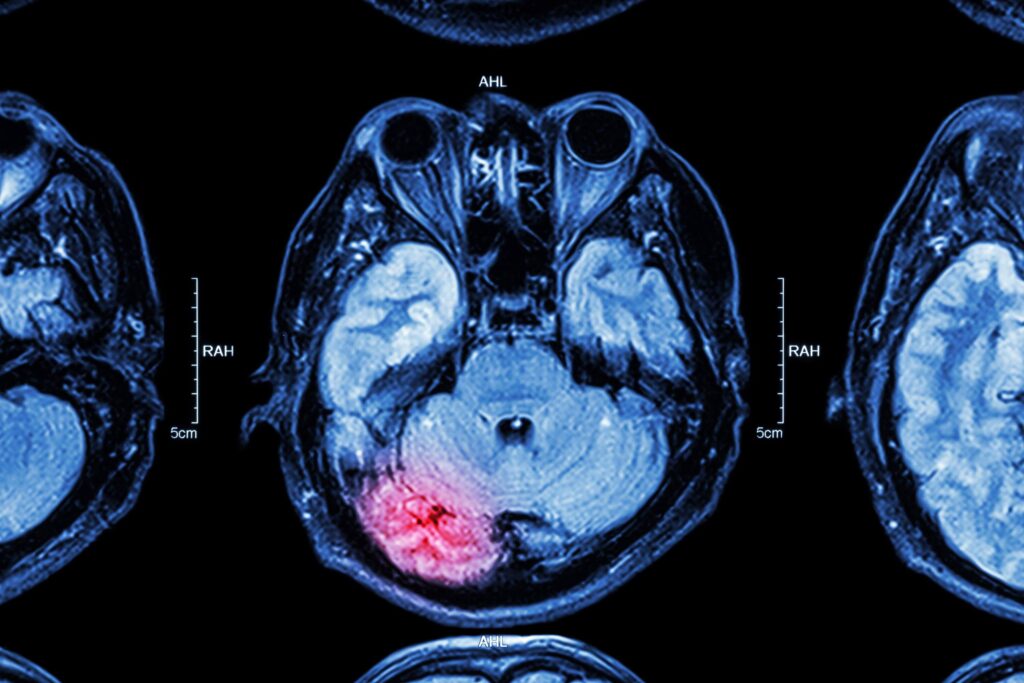
Your brain is a small but mighty organ. It makes up only 2% of your body weight but uses 20% of the oxygen you breathe. It controls everything, from breathing and digestion to language and memories—meaning an injury to this organ can lead to numerous issues.
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is any sudden injury that happens to the brain. The injury disrupts the brain’s normal functions, potentially affecting other parts of the body as well. TBIs can be mild, moderate or severe, but no matter what type of traumatic brain injury a person has, the damage to the brain occurs instantly.
What Causes Traumatic Brain Injuries?
TBIs are caused by an injury that disrupts the brain’s normal function. This can be a bump or blow to the head, or an object that pierces through the skull and damages brain tissue.
Some common causes of TBIs include:
- Assaults
- Car accidents
- Falls
- Sports injuries
It’s worth noting that not every bump on the head results in a TBI. Brain scans can help patients and providers identify a TBI after an accident or injury.
What Are the Types of Traumatic Brain Injuries?
- Concussions are the most common type of TBI. It causes shock and trauma to the brain, and it can affect your balance, memory and/or vision.
- Contusions are bruising of the brain. These are like bruises on other parts of your body, in that they are injured or swollen parts of the brain combined with blood leaking from blood vessels.
- Hemorrhage is bleeding in the brain, and it may occur with contusions.
- Intracranial hematomas are blood clots that occur between your skull and your brain. They can take days or weeks to show up after a TBI.
- Skull fractures are cracks within the skull. These can potentially cause broken bones to cut into the brain, causing further damage.
What Are the Symptoms of a Traumatic Brain Injury?
The symptoms of a TBI will depend on its type and severity. Some symptoms happen immediately after the traumatic event, but others may appear days or weeks later.
People with mild TBIs may experience symptoms including:
- Blurred vision
- Confusion
- Head or neck pain
- Mood changes
- Sleep disturbances
- Slowed reflexes
Usually, mild symptoms will subside after a few days or weeks.
People with moderate or severe TBIs often experience the same symptoms as mild injuries, but may also experience the following symptoms as well:
- Dilation of the eyes
- Drainage of bloody or clear fluid from the ears or nose
- Memory problems
- Numbness or weakness of the limbs
- Trouble speaking, walking, or waking up
- Seizures
- Slurred speech
Medical Imaging Exams Used to Diagnose Traumatic Brain Injuries
A provider will ask about the details of the injury and what symptoms the patient is experiencing. They will do a neurologic exam to test for any damage to the brain, nervous system and/or spinal cord.
Imaging tests are often used to help diagnose TBIs. CT scans of the head are especially useful, as they can create images of bone and soft tissue. MRI scans can help monitor swelling in the brain, and PET scans show brain function, not just brain structure.
Can Traumatic Brain Injuries Be Treated?
Yes, they can. A mild TBI can be treated with rest. Over-the-counter medication can help alleviate headaches, and your provider will tell you when it’s safe to return to your normal activities.
A moderate or severe TBI may require more extensive and hands-on treatment, depending on where and how the brain was affected. These TBIs may require medication, surgery or rehabilitation.
Some TBIs may cause permanent disabilities or changes. However, proper diagnosis and treatment can help improve quality of life.
If your doctor recommends a brain scan after a traumatic brain injury, American Health Imaging offers leading-edge tests in numerous locations. Request an appointment or contact us to learn more.